By Swordfish.ai RevOps
Who this is for
- Head of RevOps or Sales Ops enriching inbound leads when the only reliable identifier is a phone number.
- SDR leaders building outbound lists and trying to avoid wrong-person outreach and deliverability problems.
- Talent Acquisition teams mapping a direct dial or cell to an email for recruiting outreach with consent and opt-out controls.
- Marketing ops running contact enrichment and enforcing email verification before sends.
Use cases
- Inbound lead enrichment: convert “phone-only” hand-raisers into a usable email record without guessing.
- Event list follow-up: backfill emails from scanned numbers, then verify before sequencing to protect deliverability.
- Recruiter sourcing: route low-confidence matches to manual review so you don’t message the wrong candidate.
- Account management: refresh stale records when job changes and reassigned numbers cause bounce and no-connect waste.
Quick Answer
- Core Answer
- To find email by phone number, treat it as identity resolution: normalize the phone, resolve the identity, match email candidates, then verify deliverability and employer alignment. Use confidence levels to decide what can be automated versus what needs review.
- Key Insight
- Phone→email is correlation (phone ↔ identity ↔ email). Match quality depends on identity inputs and recency of the underlying signals.
- Best For
- B2B outreach where you can justify contact under consent or legitimate interest, honor opt-out, and keep a suppression-first workflow.
Compliance & Safety
This method is for legitimate business outreach only. Always respect Do Not Call (DNC) registries and opt-out requests.
Use only for legitimate interest and compliant outreach. Verify matches and honor opt-out requests promptly.
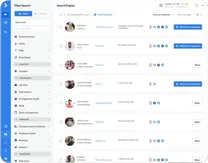
Methods overview (fast triage): Start with a phone number to email finder workflow to reduce manual research time and avoid wrong-person outreach, confirm employer/domain signals, and finish with verification. Manual checks (company contact pages or professional profiles) are the fallback when confidence is not high enough to automate.
- Tool-based cross‑lookup: best when you have phone + at least one identity field.
- Company-domain inference: best when you know employer and need to confirm alignment.
- Professional profile corroboration: best for Medium confidence matches before CRM write.
- Company contact pages: best for shared numbers or front-desk routing.
- Manual confirmation: best when a mismatch would create compliance or brand risk.
Framework: The Cross-Lookup Flow: Identify → Match → Verify → Use
- Identify: normalize phone + add context for identity resolution.
- Match: generate email candidates from the resolved identity.
- Verify: email verification + phone number verification (signal validation) before activation.
- Use: route by confidence levels and respect consent/opt-out.
Step-by-step method
- Identify (make the phone usable and reduce ambiguity)
- Normalize to E.164 (country code + number). Bad formatting causes false “no matches.”
- Add context: name, company, company domain, location, role. Better identity resolution reduces collisions.
- Match (run cross‑lookup and capture candidates)
- Run phone → identity → email matching as contact enrichment. Treat results as candidates, not truth.
- Record metadata (name, employer, domains, any confidence indicator). You need it for routing and audits.
- Verify (protect deliverability and avoid contacting the wrong person)
- Email verification: check deliverability signals before any sequence or campaign.
- Phone number verification: use a real-time connectivity check / signal validation when available to reduce disconnected or reassigned line risk.
- Signal validation lowers risk; it does not prove current ownership.
- Use (route by confidence levels)
- High confidence: write to CRM and allow compliant sequencing with opt-out.
- Medium confidence: require one corroboration step before automation.
- Low confidence: do not sequence; do manual confirmation or skip.
Three worked examples (inputs → confidence → action)
- Input: phone + full name + company domain → Confidence: High when employer aligns and email verification passes → Action: write to CRM and sequence.
- Input: phone only; result routes like a shared company number → Confidence: Low → Action: do not write; find the correct person before outreach.
- Input: phone + name; email domain differs from stated employer → Confidence: Medium/Low depending on signals → Action: corroborate via professional profile or company site, then re-verify.
Decision Heuristic
Before you contact anyone: if this match is wrong, what is the real cost for your team—deliverability damage, brand risk, or a compliance complaint?
Confidence levels: a routing legend
- High: identity matches (name + employer/domain) and verification signals are clean → safe for automation with opt-out.
- Medium: partial identity match or inconclusive verification (for example, catch-all domains) → manual review or a confirmation step, not high-volume sequencing.
- Low: weak identity resolution (shared numbers, conflicting employer, missing context) → keep out of sequences; do not write to CRM as “confirmed.”
If you’re building the full record, pair this workflow with phone number lookup and, when you suspect it’s a personal line, validate it with cell phone number lookup.
Checklist: Weighted Checklist
This checklist prioritizes actions that improve match quality without pretending certainty. Weighting is based on common failure points: ambiguity in identity resolution, stale signals, and unverified deliverability.
- Highest impact: Add context fields (name + company/domain + location) before lookup to improve identity resolution.
- Highest impact: Gate automation using confidence levels (High/Medium/Low) with clear downstream rules.
- High impact: Require email verification before any sequence write.
- Medium impact: Normalize phone format and country code to reduce false misses.
- Medium impact: Add phone number verification (connectivity / signal validation) when available to reduce reassigned/disconnected waste.
- Medium impact: Standardize daily enrichment capacity with unlimited contact credits so teams don’t skip verification to conserve credits.
Decision Tree: Conditional Decision Tree
- If you only have a phone number, then add at least one identity field (name or company/domain or location) before lookup to improve identity resolution.
- If the lookup returns multiple candidates, then pick the one with consistent employer/domain alignment and verification signals; store alternates as secondary candidates.
- If email verification is inconclusive, then treat the result as Medium confidence and avoid high-volume sending.
- If the number appears to be VoIP or routes like a main line, then downgrade confidence and require corroboration before any CRM write.
- Stop Condition: If you cannot justify outreach under consent or legitimate interest, or you cannot operationally honor opt-out and suppression, stop. Do not enrich, store, or message.
Diagnostic: Why this fails
Most failures fall into two buckets: weak identity resolution (not enough context, shared numbers) and recency decay (reassignment, job changes). Shared numbers are often front desk or call-routing lines, which makes wrong-person matches common if you automate too early.
You don’t fix that with more volume. You fix it with confidence levels, verification, and suppression discipline.
Troubleshooting Table: Diagnostic Table
| Symptom | Root Cause | Fix |
| No match returned | Missing context; formatting/country mismatch; no available signals | Normalize to E.164; add name/company/domain/location; retry; if still empty, do manual confirmation before outreach |
| Wrong person returned | Shared numbers (front desk), reassigned lines, identity collisions | Require employer/domain alignment and verification; downgrade confidence; avoid automation until corroborated |
| Email bounces | Stale record; role-based inbox; catch-all domain hides mailbox status | Run email verification; if catch-all/inconclusive, keep at Medium and use a confirmation step before sequences |
| Phone disconnected/unreachable | Reassignment or carrier routing change | Run phone number verification with signal validation; re-enrich later; do not assume current ownership |
| Multiple emails returned | Job changes, multiple domains, aliases | Select by employer match and verification; store alternates; timestamp your choice |
How to improve results
- Operate like it’s identity resolution, not lookup. Cross-lookup is correlation: phone ↔ identity ↔ email. Add context to reduce collisions.
- Separate enrichment from activation. Enrich first, verify second, activate only when confidence levels support it. This limits deliverability risk and wrong-person outreach.
- Define your merge policy. Decide when enrichment can overwrite CRM fields, when it appends, and when it creates a review task. Don’t overwrite rep-confirmed emails without review. Put the rules in your data quality standard.
- Plan for recency decay. Results depend on identity resolution + recency. Re-enrich priority segments on a cadence instead of assuming old records stay true.
- VoIP variance is real. When a line routes like VoIP or a main line, use stricter gates. Treat it as higher risk for wrong-person contact.
Legal and ethical use
- Consent and legitimate interest: Only enrich and contact when you can justify outreach for a legitimate business purpose.
- Opt-out: Every outbound channel needs a clear opt-out, and opt-out must suppress future enrichment and messaging.
- Not for sensitive decisions: Do not use contact enrichment to make decisions about employment eligibility, credit, housing, or other sensitive determinations.
- Regional note: US/Canada and EU outreach norms differ. If you operate across regions, align your process to the strictest rule set your counsel approves.
- Do not: Harass, impersonate, or bypass platform restrictions to obtain contact details.
For baseline privacy expectations and enforcement posture, use FTC guidance as a reference point: FTC privacy & security guidance.
Evidence and trust notes
- Last updated: Jan 2026
- Variance explainer: Match rates move with identity inputs (name/company/location), signal recency (job change, reassignment), and carrier type (mobile vs VoIP).
- Verification language: “Real-time connectivity check” and “signal validation” reduce risk; they do not prove current ownership.
- Auditability: Store source, timestamp, confidence level, and verification outcomes per record so mistakes can be traced and fixed.
- Operational trust signal: Central suppression lists (opt-out/DNC/internal do-not-contact) must be enforced by default.
- Deliverability basics explainer: Cloudflare on email authentication.
Implementation Notes
- Visuals to add (checklist):
- Cross‑Lookup Flow diagram: Identify → Match → Verify → Use
- Confidence badge legend (High/Medium/Low) with routing actions
- Example CSV template screenshot showing columns: phone, first_name, last_name, company, domain, location, linkedin_url
- Schema notes: FAQPage and Article schema; BreadcrumbList if your site template renders breadcrumbs.
- Tracking: Track “File Upload start / enrichment run” plus downstream quality: bounce rate, reply rate, suppression hits, and mismatches flagged by reps.
- Priority ops note: If you’re doing call-list triage, your queue should be ranked mobile numbers by answer probability so reps spend time where connects are plausible.
Next steps
- Day 1: Define confidence levels and routing rules (what writes to CRM, what requires review, what gets suppressed). Align this with data quality.
- Day 3: Run a small batch enrichment from a CSV with these columns: phone, first_name, last_name, company, domain, location, linkedin_url. Example row: +14155551212,Jane,Doe,Acme Inc,acme.com,San Francisco,https://linkedin.com/in/janedoe. Expected outputs: email candidate(s), confidence level, verification status, and a timestamped source note. Write outputs to CRM fields: email, confidence_level, email_verification_status, and source_timestamp.
- Day 7: Scale bulk enrichment and ensure your call queues are ranked mobile numbers by answer probability. If you need stable day-to-day throughput, set expectations around unlimited contact credits.
FAQ
Is it possible to find an email from a phone number?
Yes, if the phone can be correlated to an identity record and that identity can be matched to an email. It’s not guaranteed because shared numbers, reassignment, and missing signals can break the chain.
Why do matches come back wrong?
Most wrong matches come from identity collisions (shared numbers), stale signals (reassigned numbers, job changes), or weak inputs (no name/company/location). Route by confidence levels and verify before you automate.
How do I verify an email before outreach?
Run email verification and confirm employer/domain alignment. If verification is inconclusive (for example, a catch-all domain), keep it at Medium confidence and avoid high-volume sequences.
Is phone-to-email lookup legal?
It can be, depending on jurisdiction and your lawful basis. Operationally, the minimum standard is: only contact for legitimate business reasons, respect DNC rules for calling, and honor opt-out requests quickly.
What if a number is VoIP?
VoIP routing increases variance because numbers can be shared or forwarded. Treat VoIP signals as higher risk and require corroboration before marking a match as High confidence.
Can I do this in bulk?
Yes. Bulk is where process discipline matters: include context fields, enforce merge rules, verify before activation, and suppress opt-outs centrally. For daily workflows, unlimited contact credits avoids rationing that leads to skipping verification.
What does “confidence” mean here?
Confidence is your operational estimate that the phone ↔ identity ↔ email correlation is correct, based on alignment signals and verification outcomes. It should control downstream actions (automate, review, or stop).
How do I handle opt-out?
Store opt-out in one system of record (usually CRM), sync it to messaging tools, and suppress across channels. Do not re-add opted-out contacts through enrichment.
Is reverse phone to email reliable?
Reverse phone to email is reliable when identity resolution has enough context and you route results by confidence levels. If your inputs are thin or signals are stale, treat matches as candidates until verified.
Related workflows: use email address lookup and locator when you start with email and need to complete the record, or phone number lookup when you need more context on the line you’re working with.
Neutral references: FTC privacy & security guidance, ICANN WHOIS information, Cloudflare on email authentication.
About the Author
Ben Argeband is the Founder and CEO of Swordfish.ai and Heartbeat.ai. With deep expertise in data and SaaS, he has built two successful platforms trusted by over 50,000 sales and recruitment professionals. Ben’s mission is to help teams find direct contact information for hard-to-reach professionals and decision-makers, providing the shortest route to their next win. Connect with Ben on LinkedIn.


 View Products
View Products