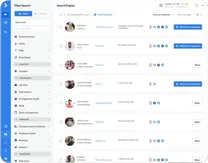
- Core Answer
- Sales intelligence tools are the systems in your sales tech stack that help teams source target accounts, enrich records with verified contact and company data, rank who to work first, sequence outreach across channels, and measure outcomes that drive time to connect and pipeline velocity.
- Metric to manage
- Time to Connect: the elapsed time from when a lead/contact enters an SDR queue to the first live conversation with the intended decision-maker, tracked alongside connect rate and meetings per attempt.
- Ideal role owner
- Sales Ops/RevOps owns tool selection, CRM writeback rules, data quality, and the measurement plan; SDR leadership owns sequence adherence, dispositions, and coaching.
Sales Intelligence Tools (2026): The Modern Stack Map
By: VP of Sales Operations
Last updated: Jan 2026
Who this is for
- Sales Ops and RevOps leaders standardizing a sales tool stack to reduce time to connect and improve pipeline velocity.
- SDR/BDR leaders who need more live conversations per hour without inflating headcount.
- Revenue leaders replacing overlapping point solutions with a workflow-based stack: source, enrich, rank, sequence, measure.
- SaaS outbound teams with phone-first motions where mobile coverage and pricing model determine activity volume.
Quick Answer
- Definition: Sales intelligence tools support outbound by organizing the workflow from target selection to verified reachability, prioritization, orchestration, and reporting.
- Recommended structure: Use a sales tool stack with defined jobs per layer: source-enrich-rank-sequence, then measure outcomes so tool decisions tie to time to connect and pipeline velocity.
- Best tools by layer: The best sales intelligence tools are the ones that do one job cleanly in your workflow (source, enrich, rank, sequence, measure) and reduce dead-end attempts so first conversations happen sooner.
The best sales intelligence stack is built around your workflow: source targets, enrich with high-quality contact data, rank by likelihood, sequence outreach, and measure outcomes like connect rate.
Compliance & Safety
This method is for legitimate business outreach only. Always respect Do Not Call (DNC) registries and opt-out requests. Ensure your outreach and data use are compliant; honor opt-out and applicable consent rules.
How this works (in practice)
Pipeline velocity is a workflow outcome: how quickly records move from new target to first conversation to meeting to opportunity created. Sales intelligence tools affect velocity by reducing wrong-number attempts, minimizing manual cleanup, and making prioritization and execution consistent.
Framework: Sales Tool Stack: Source → Enrich → Rank → Sequence → Measure
- Source: build an ICP-correct universe (accounts and personas) with filters that match territory and routing rules.
- Enrich: attach deliverable email plus verified mobile/direct lines; write back cleanly to CRM with field ownership.
- Rank: prioritize who to work today using fit, signal, and reachability constraints.
- Sequence: execute outreach steps with governance on timing, call attempts, stop rules, and dispositions.
- Measure: report time to connect, connect rate, meetings per attempt, and data quality failure points by segment.
In a stack review, I expect each layer to produce an artifact I can audit:
- Source: an exportable target universe with consistent ICP and territory rules.
- Enrich: reachability fields (mobile/direct and deliverable email) with provenance and refresh behavior.
- Rank: a prioritized worklist with clear logic and adoption.
- Sequence: governed touches with required dispositions so measurement isn’t based on partial logs.
- Measure: a closed-loop view that ties outcomes back to source and enrichment inputs for remediation.
To align the stack to operational outcomes, I map each layer to tool types and the business outcome it supports:
- Source (sales prospecting tools): ICP databases and account discovery that reduce list-building time and keep territories consistent.
- Enrich (contact data tools): enrichment tools and direct dial providers that reduce wrong-number attempts and improve time to connect.
- Rank: prioritization that reduces time wasted on low-reachability records and improves meetings per hour.
- Sequence (outbound sales tools): sequencing that enforces steps and logging so coaching and measurement are possible.
- Measure: reporting that ties outcomes back to data quality and tool inputs so you can fix root causes instead of adding more sources.
Phone-first outbound has two operating rules:
- “Use ranked mobile numbers by answer probability to call the best number first.”
- “A true unlimited, fair-use model prevents reps from rationing lookups and calls.”
When you need to validate whether your enrichment layer supports calling outcomes, start with B2B mobile number data and confirm you can run the calling motion without rationing behavior.
Checklist: Diagnostic Table
Use this diagnostic to find the limiting step in your stack. Fix the earliest break first; that’s where time to connect usually improves fastest.
| Symptom | What it usually means | Fix (Sales Ops action) |
|---|---|---|
| Time to connect is long even with high dial volume | Reachability is weak, or reps are calling the wrong number first | Gate records on verified reachability, and implement direct dial lookup workflows that prioritize best numbers first. |
| Connect rate drops mid-month | Credit limits change rep behavior and reduce activity | Benchmark your pricing model against unlimited contact credits approaches and align plans to required activity volume. |
| Reporting is inconsistent across reps and teams | Writeback rules and dispositions are not standardized | Define required dispositions for phone outcomes (connected, voicemail, wrong number, do-not-call request) and enforce them in the sequence tool and CRM. |
| High bounce rates and duplicate records | Enrichment and hygiene are unmanaged | Put a recurring data quality audit in place and enforce dedupe and stale-field remediation. |
| SDRs work the queue randomly | Ranking is absent or not trusted | Implement a transparent ranking model that combines fit, signal, and reachability; publish the logic and validate with outcomes. |
| Strong email activity, weak calling outcomes | Sequence design doesn’t match a phone-first motion | Adopt a phone-first sequence and pair it with LinkedIn prospecting tools for parallel social touches that support calling. |
Decision Tree: Weighted Checklist
This checklist prioritizes evaluation criteria using standard outbound failure points: reachability and pricing drive activity and connects; integration and governance drive reporting integrity and repeatability.
| Selection criterion | Why it affects time to connect and pipeline velocity | Weight | Effort | How to validate in a pilot |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Verified mobile/direct coverage for your ICP | Fewer wrong numbers and faster live conversations per rep-hour | High | Medium | Enrich a cohort, run the same sequence, then compare connect outcomes to your current provider by segment. |
| Cost model supports required activity volume | Rationing slows down calling and extends time to connect | High | Low | Run a full-cycle pilot and review whether reps changed lookup/dial behavior as credits tightened. |
| CRM writeback rules (field mapping, provenance, dedupe) | Clean writeback prevents reporting noise that hides what is improving velocity | High | Medium | Write back into a sandbox and run a duplicate and overwrite audit before production. |
| Ranking combines fit + signal + reachability | Reps spend attempts on contacts that can answer, improving meetings per attempt | High | Medium | A/B test ranked vs unranked queues and review time to connect and meeting creation differences. |
| Sequence governance (steps, stop rules, dispositions) | Consistency improves coaching and makes outcome attribution reliable | Medium | Medium | Audit sequences for adherence and required dispositions; review exception rate and missing outcomes. |
| Closed-loop measurement back to enrichment and hygiene | Fixes root causes so performance doesn’t decay over time | Medium | Medium | Set a recurring review where connect failures trigger enrichment refresh or suppression rules. |
Troubleshooting Table: Scoring Rubric
Use this rubric to score a stack during selection and quarterly reviews. The objective is repeatable execution with measurable improvements in time to connect and pipeline velocity.
| Category | 1 (Weak) | 3 (Acceptable) | 5 (Strong) | Operator test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | ICP filters are broad and require cleanup | Filters match ICP; some manual review | ICP + territory rules are consistent and auditable | Build one territory list and audit for ICP fit and routing alignment. |
| Enrich | Low reachability; stale titles and inconsistent writeback | Usable reachability with periodic refresh | High-confidence mobile/direct plus consistent CRM writeback | Enrich a cohort and review connect outcomes and hygiene issues after sequences complete. |
| Rank | No prioritization; reps cherry-pick | Basic scoring; limited outcome correlation | Ranking correlates with connects and meetings and is adopted | Compare time to connect for top-ranked vs bottom-ranked contacts in a controlled queue. |
| Sequence | Ad hoc steps; inconsistent dispositions | Standard steps; drift exists | Governed steps, stop rules, and clean activity logging | Audit records end-to-end for step adherence and disposition completeness. |
| Measure | Activity metrics only | Connect and meetings tracked; limited segmentation | Closed-loop reporting tied to remediation and enablement | Trace one opportunity back to source/enrichment inputs and verify data provenance. |
Evidence and trust notes
- How this hub is differentiated: It’s organized by job in the stack (source, enrich, rank, sequence, measure) so you can remove overlap and tie each tool to a measurable output.
- Phone-first emphasis: Tool decisions start with mobile/direct reachability and pricing behavior because those two variables affect time to connect.
- Measurement-first approach: Selection and renewals should be based on controlled tests (cohorts and A/B queues) and outcome lift, not feature counts.
- Operator requirement: Require vendor documentation on data provenance and refresh behavior, then verify in a pilot with CRM writeback enabled.
- Disclosure: Swordfish.ai is a vendor; the framework and evaluation process are designed to be used with any provider.
- Compliance: Outreach guidance assumes compliant use and honoring opt-out and applicable consent rules.
Implementation Notes
- Rollout order: Stabilize Enrich + Measure before adding more Source tools, or you scale bad data into more workflows.
- Field governance: Define a system of record per field (mobile, email, title, company), lock down overwrite rules, and log provenance so reporting stays stable.
- Measurement location: Publish one CRM dashboard that includes time to connect, connect rate, meetings per attempt, and opportunity creation from outbound, reviewed weekly by Sales Ops and SDR leadership.
Visuals to add
- Stack map visual: Source → Enrich → Rank → Sequence → Measure, annotated with tool types per layer and the artifact produced per layer.
- Phone-first module callout: reachability gate + ranked dialing + pricing behavior effects on time to connect.
- One-page version of the scoring rubric for procurement and QBRs.
Next steps
- Week 1 (baseline and definitions): Sales Ops defines time to connect and pipeline velocity in CRM terms, aligns required dispositions, and documents field ownership and overwrite rules.
- Weeks 2–3 (pilot design): Sales Ops builds a pilot scorecard and acceptance criteria for writeback (field mapping, overwrites, dedupe); SDR leadership commits to sequence adherence and disposition completeness.
- Weeks 4–6 (pilot execution): Run enrichment and ranking on a defined cohort, then review time to connect, connect rate, meetings per attempt, and hygiene issues triggered by real sequences.
- Weeks 7–8 (scale and governance): Promote winning writeback and ranking rules to production, document SOPs for dispositions and remediation, and schedule the first monthly data quality review.
- Main action: Use the Rubric download conversion event with the lead magnet (Rubric sheet template) so your committee scores vendors consistently and ties decisions to time to connect and pipeline velocity.
CTA: Download the Stack Evaluation Rubric
FAQs
What are the best sales intelligence tools?
The best sales intelligence tools are the ones that fill a specific job in the stack (source, enrich, rank, sequence, measure) and produce measurable improvement in time to connect, connect rate, meetings per attempt, and pipeline velocity.
Do I need an enrichment tool?
If your CRM records don’t consistently include verified mobile/direct numbers and deliverable emails, you need enrichment. Without it, more sourcing increases attempts but not live conversations, which slows time to connect.
What is a phone-first stack?
A phone-first stack prioritizes verified mobile/direct data, ranks contacts by reachability so reps call the best number first, and supports enough activity volume to sustain calling without behavior changes caused by credit constraints.
How do I evaluate tools?
Score each tool against its stack job, validate with a time-boxed pilot, and require clean CRM writeback. Use cohort tests for enrichment, A/B tests for ranking, and sequence audits for execution consistency.
What metrics matter?
Track time to connect, connect rate by segment, meetings per attempt, conversion to pipeline, and data quality indicators such as bounce rate and duplicate rate. Use those outputs to guide remediation and renewals.
About the Author
Ben Argeband is the Founder and CEO of Swordfish.ai and Heartbeat.ai. With deep expertise in data and SaaS, he has built two successful platforms trusted by over 50,000 sales and recruitment professionals. Ben’s mission is to help teams find direct contact information for hard-to-reach professionals and decision-makers, providing the shortest route to their next win. Connect with Ben on LinkedIn.


 View Products
View Products